Trichromatism
Trichromatism is a tool to convert bitmap images into vector image composed with lines of 3 colors which can then be drawn by a plotter such as the Tipibot.
A shader computes a preview of the result in real time, enabling to tweak parameters easily.
The same algorithm is then applied line by line on the CPU. This process is a lot slower, but generates the SVG file that can be sent to any machine.
Some results
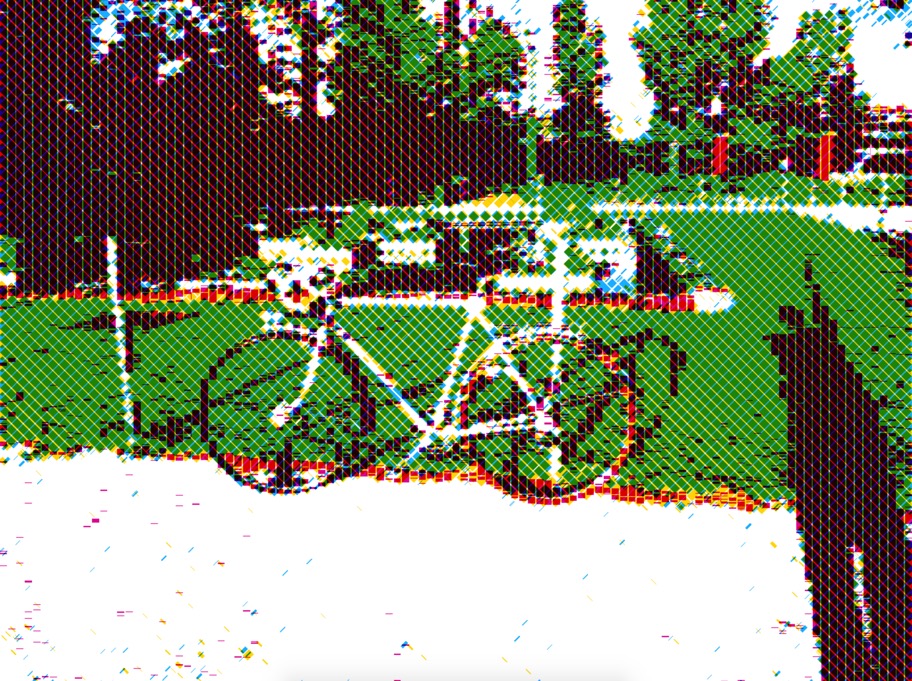
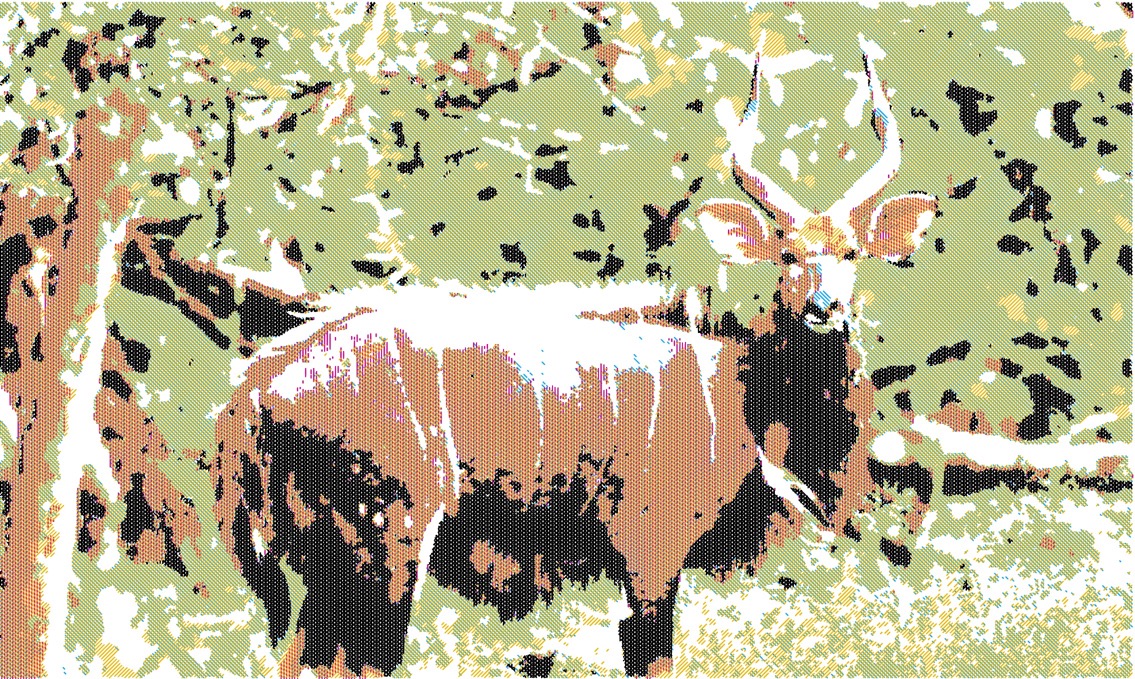



Rendering
The objective is to perform the following steps:
- compute 4 new colors from the three given colors (mix color A with color B, A with C, B with C, and the three together),
- this results in 7 colors + black and white,
- for each pixel of the image, find the closest color,
- draw a line accordingly with the appropriate angle.
The shader is quite complex.
To render the line thickness properly (to have proper end caps), I had to offset the pixel lookup as show on the following image:
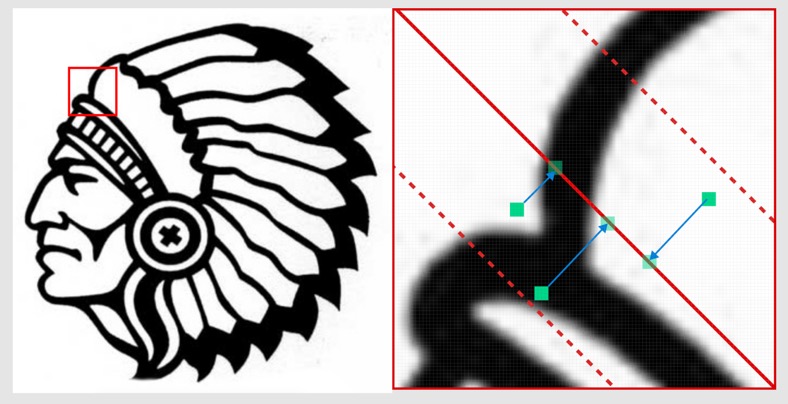
This means that the algorithm must render the image three times (one time per angle) to compute the final pixel color and draw the lines accordingly, as shown in the folling image:

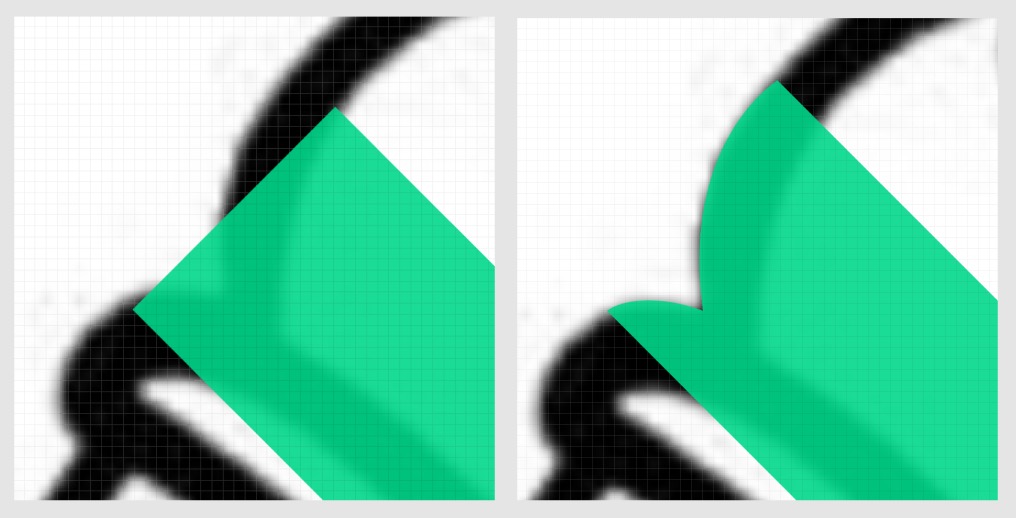
This enable to have proper line-end caps as on the left image bellow. Without offseting pixel lookups, the line caps would follow the image edges (see right image bellow). This would be cheating ;-) we would still see many details which would not be rendered with straight lines.

To compute the color difference, I used the CIE Lab - delta E* CIE94 formula from Wikipedia. I had to implement the color conversions both on the shader and the CPU algorithm.
To mix two colors, I convert their RGB values to CMYK, add them together and divide them by a given weight. The higher the weight, the lighter the colors.
Improvements
I could add different rendering modes :
- Give N colors, each with an angle, and do not mix them ; just render the closest color.
- Convert the image to CMYK, threshold each color component, and render the lines according to the resulting values. This could work with RGB values as well.
- Change the space between line according to the pixel intensities.
- Use patterns other than straight lines.
- Use a space filling curve algorithm to render the image with only 3 or 4 lines (one line for each color component).